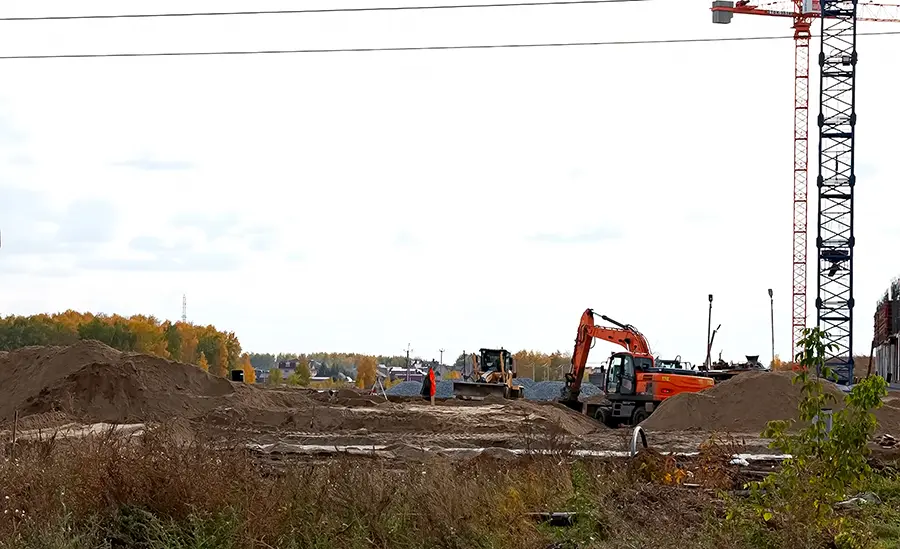
Preparing land for the construction of an electrical substation is a complex process that involves clearing, grading, excavating, and stabilizing the site to ensure it’s ready for the substantial infrastructure that substations require. Heavy equipment is essential to complete these tasks efficiently, enabling precise land preparation to support substation foundations, drainage systems, and utility installations. Below is an overview of the types of heavy machinery commonly used in preparing a substation site and the role each plays in ensuring a stable and functional foundation for the facility.
1. Excavators: Precision Digging and Trenching
Excavators are a staple in any construction project involving earthmoving and land preparation. Equipped with powerful hydraulic arms and various attachments, these machines are used for multiple tasks on substation sites:
- Trenching and Foundation Digging: Excavators are used to dig trenches for underground conduit installations, drainage systems, and foundation footings.
- Clearing and Grading: For initial land clearing, excavators remove trees, shrubs, and any obstacles that could interfere with construction.
- Attachment Versatility: By switching out the bucket attachment for augers, breakers, or hydraulic thumbs, excavators can handle various specialized tasks on substation sites, including breaking up hard soil or rock.
2. Bulldozers: Heavy-Duty Clearing and Grading
Bulldozers are critical for clearing large volumes of land and leveling surfaces. These machines have a large front blade that can push, level, and compact soil to create a stable surface for construction.
- Land Clearing and Surface Preparation: Bulldozers are used to clear vegetation, debris, and topsoil, creating a flat surface for further construction.
- Rough Grading: For substation sites requiring even terrain, bulldozers help with rough grading, making the ground level and ready for finer grading adjustments.
- Backfilling: After trenches or foundations are dug and components installed, bulldozers are also used to backfill soil and ensure a smooth finish.
3. Motor Graders: Precision Leveling and Smoothing
Motor graders are essential for creating a smooth, even surface after initial grading. Their long, adjustable blade can make fine adjustments to the ground level, making them indispensable in achieving the precise grading required for substation projects.
- Fine Grading: Motor graders provide precise leveling for areas where foundations or conduits will be placed, ensuring consistent ground conditions.
- Drainage Slope Creation: For substations, proper drainage is crucial. Motor graders help create subtle slopes in the ground, directing water away from critical equipment and reducing flood risks.
- Gravel Road and Pathway Creation: If the substation requires access roads, motor graders can spread and level gravel, creating stable paths for construction vehicles and later for maintenance crews.
4. Backhoes: Versatile Digging and Lifting
Backhoes are versatile, multipurpose machines equipped with a digging bucket on one end and a loader on the other. They are useful for smaller excavation tasks and for loading or moving materials around the site.
- Trenching for Conduits and Ground Grids: Backhoes are used to dig smaller trenches, making them ideal for installing conduits or grounding grids required in substations.
- Material Handling: Backhoes can easily transport materials like sand, gravel, and other construction materials to where they are needed on-site.
- Tight-Space Work: For projects with limited maneuvering space, such as compact substations, backhoes provide versatile digging and moving capabilities in confined areas.
5. Skid Steers and Compact Track Loaders: Small-Space Utility Work
Skid steers and compact track loaders are agile, multipurpose machines that can handle a range of tasks, especially in confined spaces or areas requiring precision.
- Small-Scale Grading and Leveling: Skid steers are often used for small-scale grading and leveling tasks, such as around foundations or in tighter spaces where larger equipment may not fit.
- Material Movement: These loaders can transport materials like gravel, soil, and sand to support larger equipment in preparing the substation site.
- Attachments for Specialized Work: Skid steers can be equipped with various attachments, such as augers, trenchers, and grapple buckets, to handle digging, trenching, or debris removal.
6. Compactors and Rollers: Stabilizing the Ground
Compactors, also known as rollers, are used to compress and stabilize soil, gravel, and other base materials, providing a firm foundation for the substation’s heavy equipment and structures.
- Soil Compaction for Foundations: Proper soil compaction is critical to prevent settling that could compromise the stability of the substation’s foundation. Rollers press the soil down to create a firm, level base.
- Gravel and Aggregate Compaction: Compactors are used to flatten and compress gravel surfaces, creating stable paths and surfaces that reduce erosion and improve stability.
7. Cranes: Lifting and Positioning Heavy Components
Cranes are often required in substation construction to lift and place large materials and components like precast walls, foundations, and equipment shelters.
- Precast Concrete and Wall Installation: Many substations use precast walls or concrete elements that are too heavy to move manually. Cranes lift and position these elements precisely.
- Heavy Equipment Placement: Substation components such as transformers and switchgear are large and heavy. Cranes assist with their placement and installation, ensuring they’re positioned accurately and safely.
8. Directional Boring Machines: Underground Utility Installation
Directional boring machines, also known as horizontal drilling rigs, are used to install underground conduits and pipelines without disrupting the ground surface. For substations, this can be essential for installing underground electrical conduits and utilities.
- Underground Conduit Installation: Directional boring allows for the installation of conduits beneath the surface without the need for extensive open trenching, which can disrupt the surrounding environment.
- Reducing Surface Disturbance: By using directional boring, contractors can install utilities with minimal impact on the surrounding area, preserving surface integrity while laying necessary infrastructure.
9. Dump Trucks: Hauling Materials to and from the Site
Dump trucks are vital for transporting large volumes of soil, debris, gravel, and other materials to and from the substation site.
- Material Removal and Disposal: Dump trucks are used to haul away excavated soil, vegetation, and debris from the cleared area.
- Delivery of Construction Materials: They also transport essential materials like sand, gravel, and backfill material, supplying what’s needed for grading and foundation work.
Heavy equipment is essential for preparing land for the construction of electrical substations, each piece of machinery playing a crucial role in clearing, leveling, excavating, and stabilizing the site. From excavators for precision digging to compactors for stabilizing soil, these machines ensure that the substation site is prepared to support reliable power infrastructure. The strategic use of this equipment ensures efficient, safe, and precise site preparation, setting the stage for a successful substation project that will serve the power needs of communities for years to come.